
In a series of studies (1-3) from the University of Missouri, the activated form of vitamin D (calcitriol) was shown to reduce TNF-α (pro-inflammatory cytokine) and increase IL-10 (anti-inflammatory cytokine).
These in-vitro studies examined the effect calcitriol had on cultured canine leukocytes when exposed to lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Leukocytes possess the vitamin D receptor (VDR) along with other cells and organs, such as intestines, kidney, spleen, and skin (4), and are capable of converting 25-OHD to calcitriol intracellularly. Leukocytes are key elements in the innate immune response.
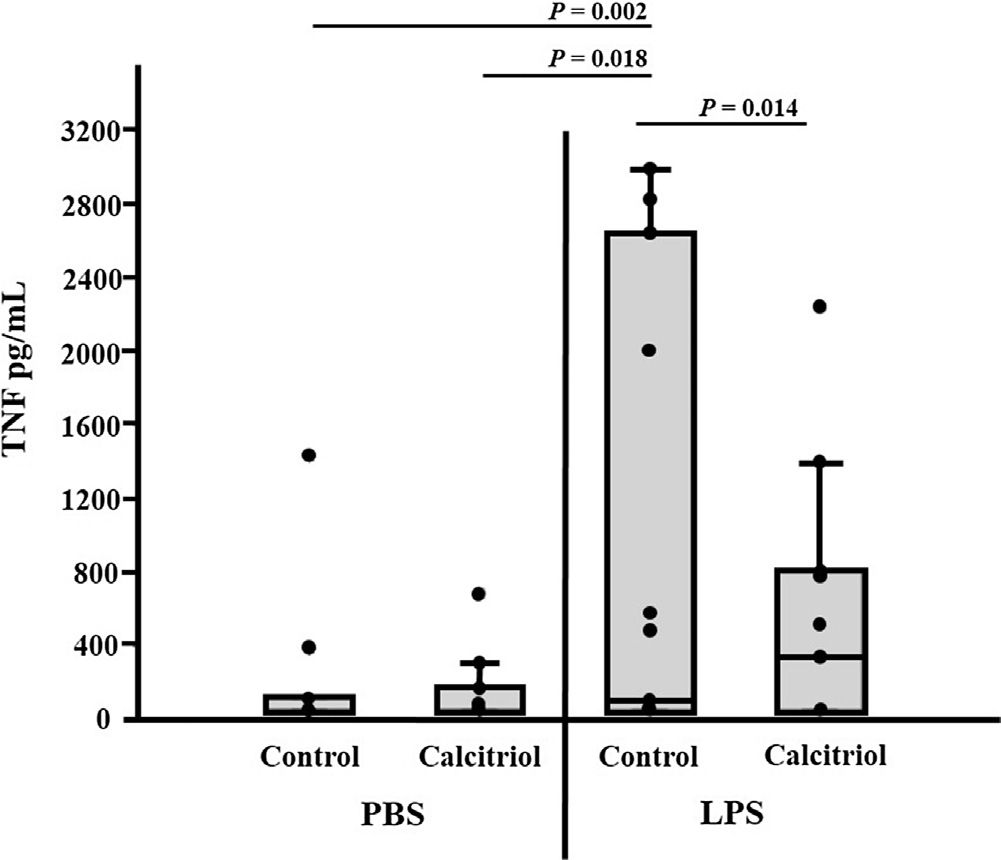
Key Finding:
Calcitriol decreased LPS-stimulated production of tumor necrosis factor in blood from critically ill dogs.
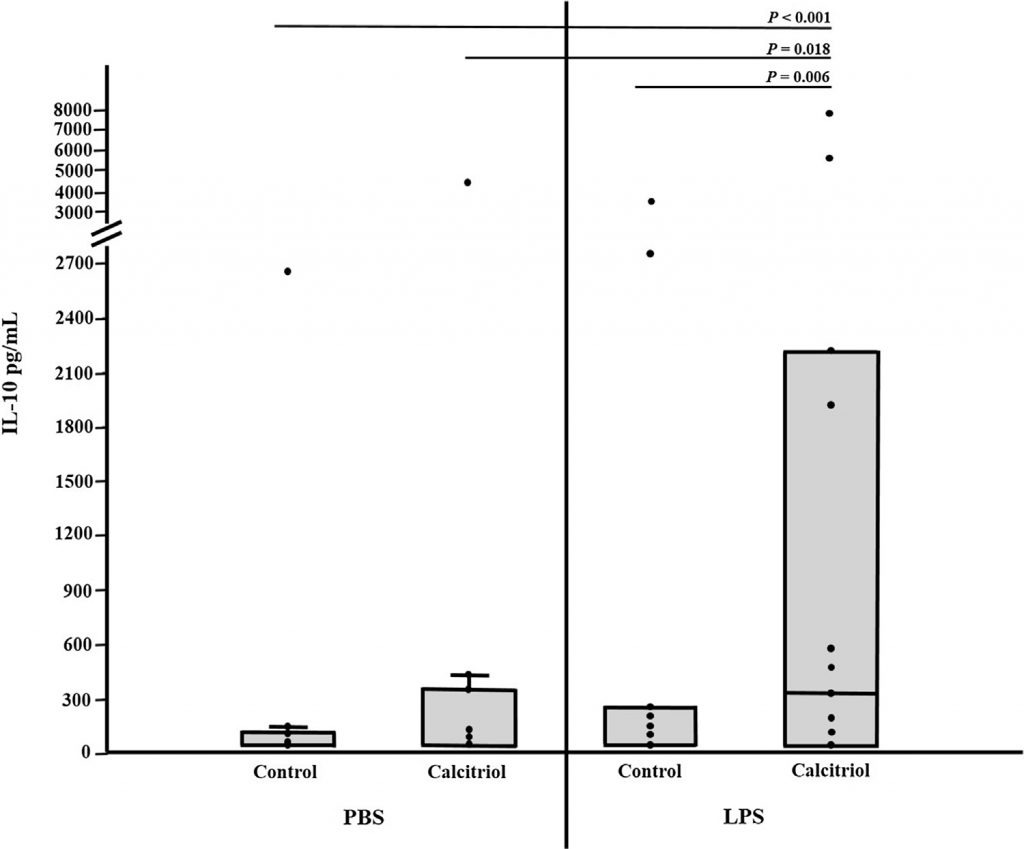
Key Finding:
Calcitriol increased LPS-stimulated production of interleukin-10 in blood from critically ill dogs.
As expected when leukocytes are exposed to LPS, TNF-α rises significantly. However in the presence of calcitriol, IL-10 rises and TNF-α decreases helping to modulate the inflammatory response.
The studies also demonstrated that in septic canine leukocytes, calcitriol can modulate the inflammatory cytokine production (which causes tissue damage in sepsis) without affecting neutrophil viability (fortify microbial killing). These findings also support the significant pruritus reduction in atopic dermatitis when dogs are supplemented with vitamin D (5).
References:
- Jaffey J (2018) Effect of calcitriol on in vitro whole blood cytokine production in critically ill dogs. Vet Journal
- Jaffey J (2018) Effect of calcitriol on phagocytic function, toll-like receptor 4 expression, and cytokine production of canine leukocytes. AJVR
- Jaffey J (2018) Effect of calcitriol on apoptosis, toll-like receptor 4 expression, and cytokine production of endotoxin-primed canine leukocytes. AJVR
- Cartwright J (2018) Vitamin D receptor expression in dogs. J Vet Int Med
- Klinger C (2018) Vitamin D shows in vivo efficacy in a placebo-controlled, double-blinded, randomized clinical trial on canine atopic dermatitis. Vet Record
